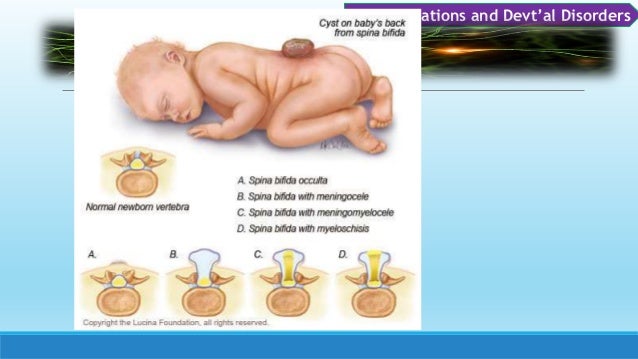
Spina bifida is a congenital condition in which the spinal cord and its protective covering do not develop properly. This can result in varying degrees of physical impairment, such as paralysis or weakness in the lower extremities, bladder or bowel dysfunction, and/or mobility challenges. Physiotherapy can be an effective treatment option for children with spina bifida to improve their mobility, strength, and overall physical function.
Here are some common physiotherapy techniques used for pediatric spina bifida:
Strengthening exercises: These exercises can help improve muscle strength, which is important for mobility and overall physical function.
Gait training: Gait training involves exercises to help improve a child's walking pattern and mobility.
Balance training: Balance training can help improve a child's balance and reduce the risk of falls.
Stretching exercises: These exercises can help improve flexibility and prevent muscle tightness, which is common in children with spina bifida.
Assistive devices: Physiotherapists may recommend assistive devices, such as braces or crutches, to help improve mobility and reduce the risk of injury.
Bladder and bowel management: Physiotherapists can also provide guidance and exercises to help improve bladder and bowel function, which is often impacted in children with spina bifida.
It's important to work with a physiotherapist who has experience working with children with spina bifida, as they will be able to create an individualized treatment plan based on the child's specific needs and abilities. Additionally, early intervention is key for children with spina bifida, so starting physiotherapy as early as possible is recommended to help improve long-term outcomes.


