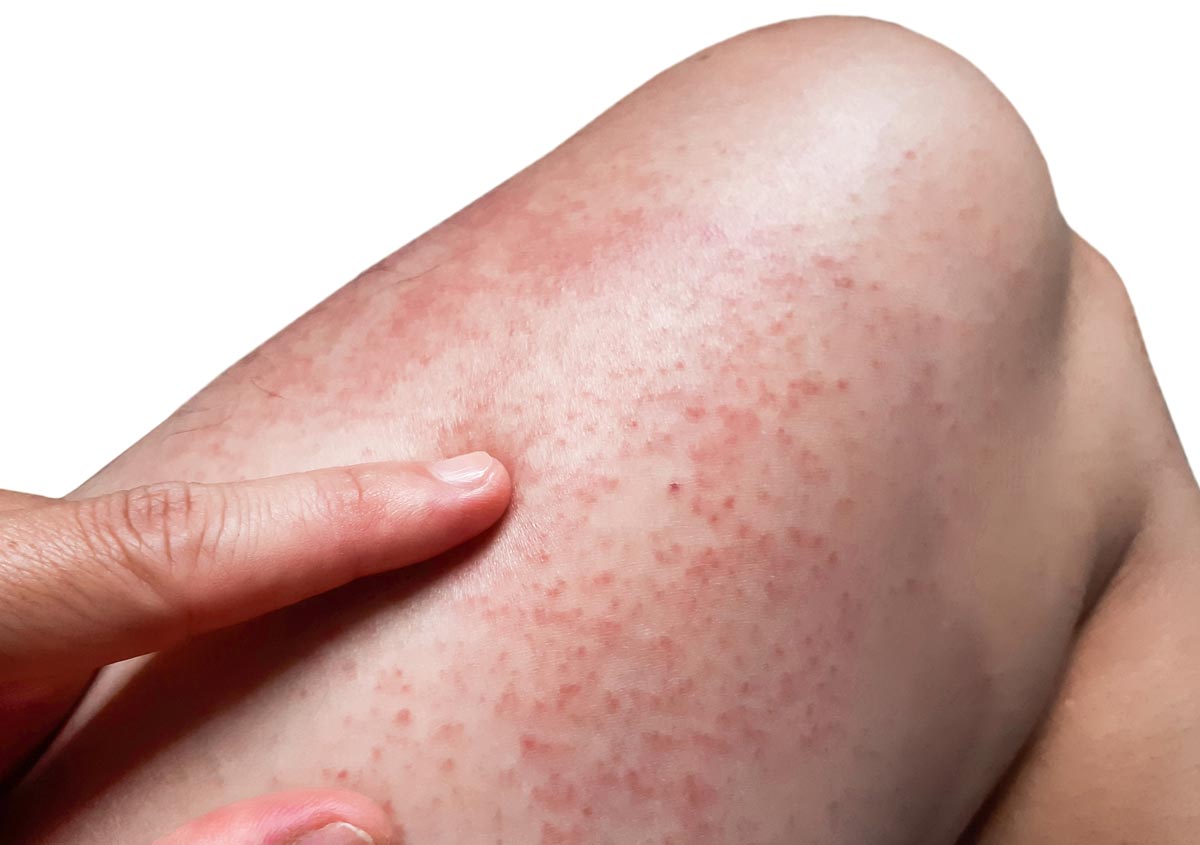
Allergy is an immune system response to a substance that is normally harmless, called an allergen.
Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, certain foods, insect stings, and medications.
When an allergen enters the body, the immune system reacts by releasing histamine and other chemicals, leading to allergy symptoms.
Allergy symptoms can vary but may include sneezing, itching, nasal congestion, watery eyes, rashes, hives, or even severe reactions like anaphylaxis.
Allergies can be diagnosed through medical history, physical examination, allergy testing (skin tests or blood tests), or food challenges.
Treatment options for allergies include avoiding allergens, taking over-the-counter or prescription medications (antihistamines, nasal sprays, etc.), immunotherapy (allergy shots), or using epinephrine for severe allergic reactions.
Allergies can be managed by identifying triggers, keeping environments clean, using air filters, and taking preventive measures.
Some allergies may resolve over time, especially in children, while others may persist throughout life.
Allergies can increase the risk of developing other conditions, such as asthma or eczema.
It's important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and management of allergies, especially in cases of severe or life-threatening reactions.


